Schedule a Task in (Dockerized) Symfony
Problem to Solve
You want to run a daily task to fetch data from Cesens.
keywords:
- Symfony
- Scheduler
- Messenger
- Message Handler
- Command
- Cron
- Supervisord
- Docker
- Docker Container
- Task Scheduling
- Asynchronous Tasks
Possible Solutions
There are several ways to schedule and execute recurring tasks in Symfony:
-
Use cron inside the PHP Docker container + Symfony command
- Define a cron job inside your PHP container that runs a Symfony command periodically.
- Pros: Simple to set up, no extra services required.
- Cons: Requires modifying container setup; not ideal for scaling.
-
Use a dedicated “scheduler” container + Symfony Messenger
- Run a separate container responsible for dispatching scheduled tasks using Symfony Messenger.
- Pros: Decouples scheduling from main app container; works well in Dockerized environments.
- Cons: More complex setup; requires managing a separate container.
-
Use host machine cron to run Docker commands
- Configure cron on the host machine to run Docker commands that execute Symfony commands inside the container.
- Pros: Minimal changes inside the container.
- Cons: Less portable; depends on host configuration.
-
Use a task scheduler tool like Supervisord + Symfony command
- Supervisord can manage long-running processes and periodically trigger Symfony commands.
- Used in the Bullsens project.
- Pros: Reliable for production; easier to manage multiple commands in one container.
- Cons: Adds another dependency and layer of configuration.
-
Other possibilities to explore
- Cloud-based schedulers (AWS CloudWatch, GCP Cloud Scheduler, etc.)
- Third-party Symfony bundles for cron scheduling
- Workflow or message queue orchestration tools (e.g., RabbitMQ, Kafka)
Concepts to Understand in Symfony
1. Scheduler
- In Symfony, the "scheduler" can refer to any mechanism that triggers tasks at specific times.
- Typically, this dispatches messages or triggers commands periodically.
2. Messenger
-
Symfony Messenger allows asynchronous execution of tasks via messages.
-
Components:
- Message: A data object representing a task to perform.
- Message Handler: A class that handles the message asynchronously.
-
Useful for decoupling task execution from request-response flow.
3. Command
- Symfony commands are CLI scripts that execute PHP logic.
- Example:
php bin/console app:fetch-cesens-data - Can be triggered by cron, Messenger, or Supervisord.
Concepts Outside Symfony
1. Cron
-
A Linux scheduler to run commands at specified intervals.
-
Can be configured in:
- PHP container
- Host machine
- Dedicated scheduler container
2. Supervisord
- A process control system for managing long-running processes.
- Can start Symfony commands at boot and ensure they stay running.
- Useful in Docker environments where multiple tasks need orchestration.
3. Docker
-
Containers add an extra layer of complexity for scheduling.
-
Key considerations:
- Where to run cron (inside container vs host machine)
- Managing environment variables and volumes
- Keeping tasks isolated from the main application container
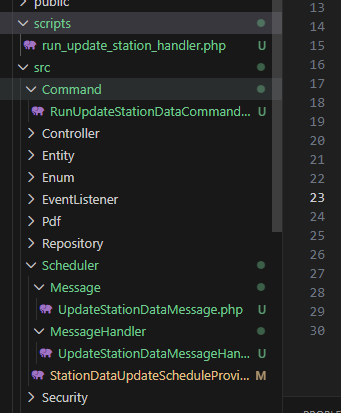
My Current Approach
I created two Docker containers for handling scheduled tasks:
- Messenger container – handles asynchronous execution using Symfony Messenger.
- Scheduler container – dispatches scheduled commands to the Messenger.
I also created:
- Symfony Command for the specific function (
app:fetch-cesens-data) - Messenger message and message handler
- Scheduler file to define the execution schedule for the task
This setup ensures the task is decoupled, scalable, and maintainable.
Architecture Overview:
Scheduler Configuration Example:
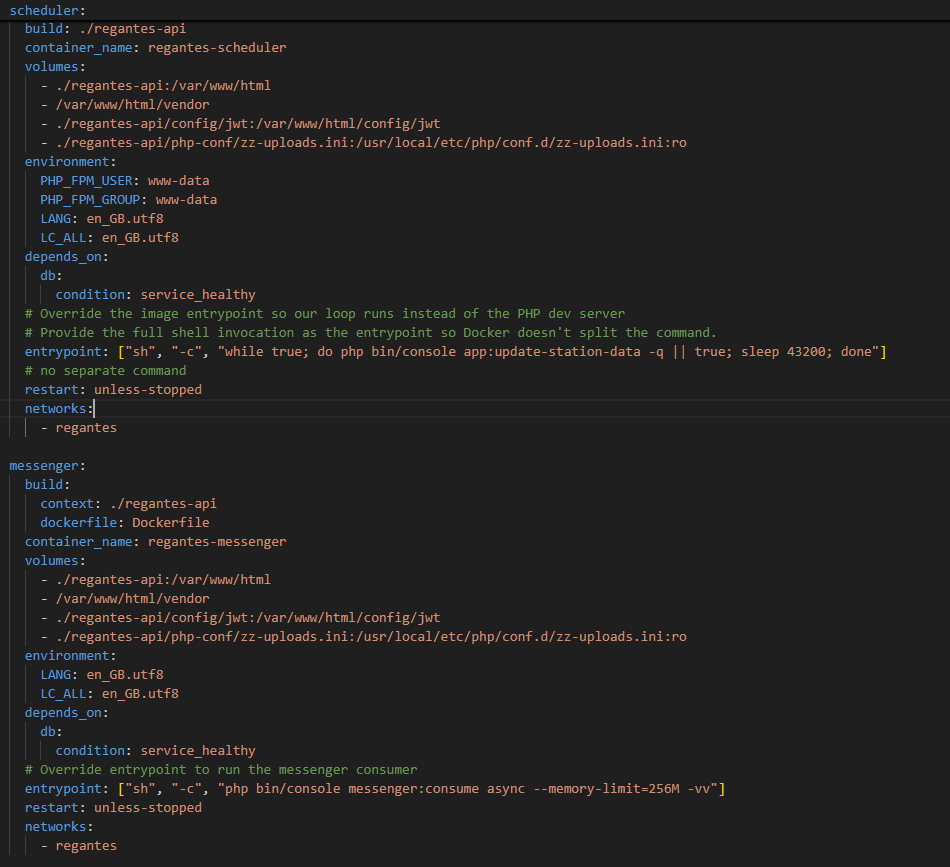
Recommended Approach
For a production-ready Symfony app in Docker, a robust approach is:
-
Create a Symfony command for your task (e.g.,
app:fetch-cesens-data). -
Use Symfony Messenger for async processing if the task is long-running.
-
Choose a scheduling mechanism:
- Supervisord inside a dedicated scheduler container (recommended for production).
- Cron inside the container (simpler for small projects).
This ensures tasks run reliably, can be monitored, and scale with your infrastructure.